1. Introduction
Table of Contents
ToggleThe global medical device industry requires accuracy, compliance, and scalability – this is what medical injection molding is good at. From disposable syringes to complex implantable parts, injection molding medical devices have become a mainstay in the production of safe and effective healthcare products.
For procurement teams in Europe and North America, the challenge often lies in finding a partner that not only masters medical plastic injection molding but also meets strict regional standards (FDA, EU MDR) and provides end-to-end support.
This guide breaks down the basic elements of medical device injection molding, helping you navigate material selection, technology, compliance, and how to choose the right supplier – whether you are expanding the production of plastic injection molding medical parts or launching custom medical devices.
2. What Is Medical Device Injection Molding?
2.1 Core Concept:
Medical device injection molding is a professional process in which medical-grade injection molding plastic is melted, and then the molten material is injected into a custom medical injection mold. Unlike standard injection molding, it prioritizes:
- Biocompatibility (ISO 10993): Ensuring that injection-molded medical plastics do not cause adverse reactions with human tissues.
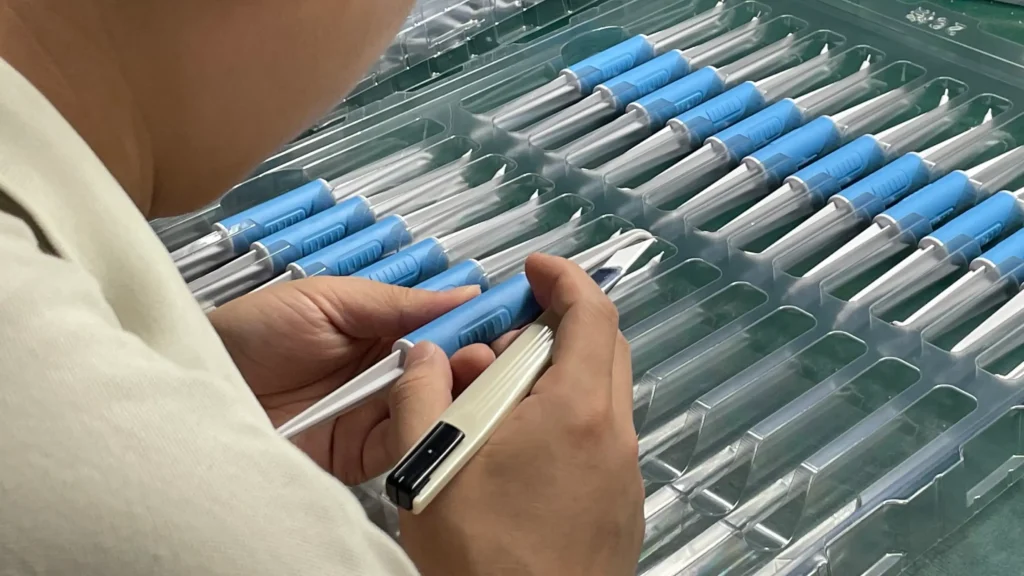
Sterile: Produced in a cleanroom medical injection molding environment (ISO 14644 Class 7/8) to eliminate contamination.
- Strict tolerance: Manufacturing injection-molded medical components with an accuracy as low as ±0.01mm, which is crucial for medical equipment.
2.2 4-Stage Process for Injection Molding Medical Devices
Clamping: The Custom medical injection mold is fixed under high pressure to prevent plastic leakage. For medical accessories, this step is of vital importance because even the tiniest gap can undermine their accuracy.
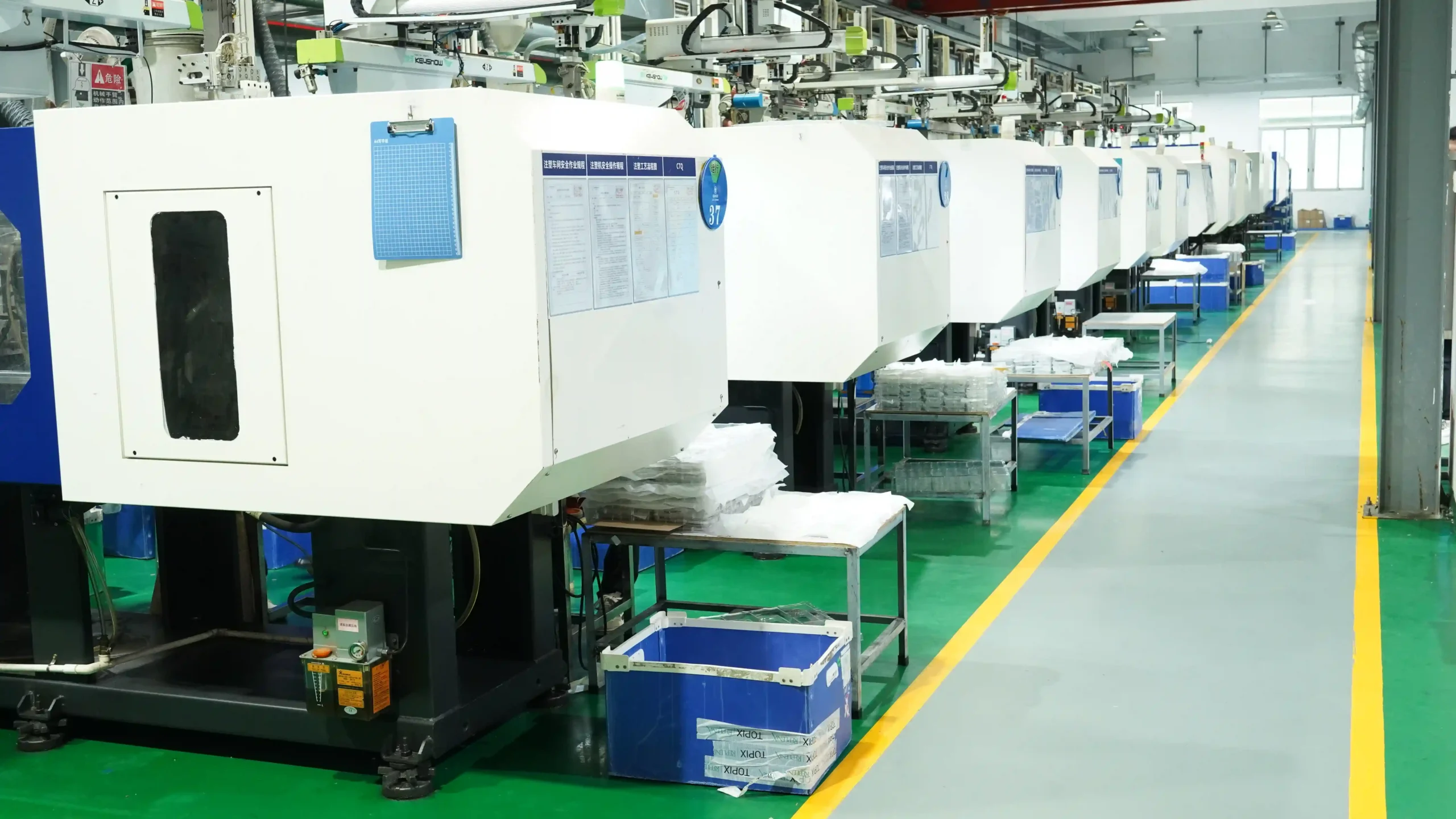
- Injection molding: Through a dedicated medical injection molding machine, molten medical-grade injection plastics (such as PP, PEEK) are injected into the mold cavity. Real-time monitoring ensures uniform flow, thereby avoiding defects that could render plastic injection molding medical parts unusable.
- Cooling: The mold is cooled to solidify the plastic, and the cooling time is customized according to the material properties. For instance, medical silicone injection molding uses LSR (liquid silicone rubber), with a curing time ranging from 30 to 60 seconds, while high-temperature-resistant PEEK requires a longer cooling time to maintain its shape.
- Ejection: The automated system will remove the medical components that have completed injection molding to minimize manual contact and maintain their sterile state. After injection, the components may be trimmed or cleaned before undergoing quality inspection.

2.3 Cleanroom Medical Injection Molding is Indispensable

3. The Role of Injection Molding in Medical Devices
3.1 High Precision of Consistency
Injection molding for medical devices offers unparalleled consistency. For instance, the inner cavity of a catheter or the electrode housing of a heart monitor relies on micro-precision injection-molded medical components, which avoids the dimensional changes that plague other manufacturing methods.
3.2 Cost-Effectiveness in Large Quantities
3.3 Outstanding Durability
3.4 Flexibility Customization
4. Key Technologies in Medical Injection Molding
| Technology Type | Core Advantage | Ideal Injection Molding Medical Parts |
|---|---|---|
| Thin-Wall Molding | Creates lightweight parts (walls <1mm); saves material for small devices | Glucose meter housings, microfluidic chips |
| Gas-Assisted Molding | Produces hollow parts with smooth surfaces; eliminates sink marks | Surgical tool handles, injection molded medical enclosures |
| Insert Molding | Bonds plastic to metal/ceramic inserts; cuts assembly steps | Dental instrument shafts, needle hubs |
| Overmolding | Adds soft layers (silicone/TPE) to rigid bases; improves usability | Oral care tool grips, syringe plungers |
| Medical Silicone Injection Molding (LSR) | Fast curing, biocompatible, and heat-resistant | Respiratory masks, catheter seals |
| Metal Injection Molding (MIM) | Creates complex metal parts (titanium/cobalt-chromium); high strength | Orthopedic screws, dental implant abutments |
| Rapid Injection Molding Medical | Shortens mold lead times (2–4 weeks); ideal for prototyping/low-volume runs | Prototype diagnostic device casings, small-batch surgical tools |
5. How to Choose Medical-Grade Injection Molded Plastics
The appropriate materials determine the safety and performance of injection-molded medical parts. The following are the top priorities for medical plastic injection molding companies:
5.1 Key Selection Criteria
Biocompatibility: Does it comply with ISO 10993 or USP Class VI? It is crucial for injection molding medical plastics that come into contact with human tissues.
- Sterilization resistance: Can it withstand autoclaving, gamma radiation, or ethylene oxide? For instance, PP is suitable for autoclaving tools, while PFA can resist harsh chemicals.
- Mechanical requirements: strength (PEEK for implants), flexibility (LSR for seals), or transparency (PC for device Windows).
- Regulatory compliance: Has it been approved in your target market (FDA in the United States, EU MDR in Europe)?
5.2 Top Medical-Grade Injection Molded Plastics
- Polypropylene (PP): Cost-effective, heat-resistant, and an ideal plastic injection molded medical component (e.g., syringes, surgical trays).
- Polyetheretherketone (PEEK): Super durable and biocompatible, it is used for orthopedic implants and is the preferred choice for injection molding of medical devices that require long-term reliability.
- Silicone (LSR): Soft, hypoallergenic, it serves as the foundation for medical silicone injection molding and is highly suitable for use in respiratory masks and catheter sealing.
- Polycarbonate (PC): Transparent, impact-resistant; Used for injection-molded medical enclosures, such as oxygenator Windows.
- Polyethylene (PE): Flexible (LDPE for pipes) or rigid (HDPE for medicine bottles); Ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene provides wear resistance for orthopedic linings.

6. Regulations on Medical Injection Molding
6.1 Global Quality: ISO 13485
- A documented QMS (Quality Management System) for every step: from medical injection mold design to cleanroom medical injection molding.
- Complete traceability of injection molding medical parts: Tracking and auditing of materials, personnel, and production batches.
Risk management: Identify hazards (such as material contamination) before production and mitigate them.

6.2 Regional Rules: FDA & EU MDR
- FDA (U.S.): High-risk devices (e.g., implants made via injection molding for medical devices) require PMA (Pre-Market Approval), while low to medium-risk components (for example, syringes) need 510(k) approval. The FDA also inspects cleanroom medical injection molding facilities to ensure sterility.
- EU MDR (European Union): Classify devices by risk (I, IIa, IIb, III). All of these require UDI (Unique Device Identifier), and medical components used for high-risk devices, such as pacemakers, need to undergo strict performance testing.
6.3 Quality Control for Best Plastic Injection Molding Medical Parts
- Monitor the temperature/pressure during the injection molding process of medical devices using real-time sensors.
Verify the sterilization process to confirm that it can eliminate pathogens.
- Use CMMs (Coordinate Measuring Machines) to check the tolerances of injection molding medical parts.
7. Common Applications of Injection Molding Medical Devices
7.1 Diagnostic Devices
- Glucose meters: Housings (injection molded medical enclosures) and test strip ports.
- Rapid test kits: Sample wells and casings.
7.2 Surgical & Dental Tools
- Dental instruments: Scalers, forceps (often made via insert molding).
- Surgical tools: Laparoscopic components, retractors (custom medical injection molding for ergonomic grips).
7.3 Disposable Supplies
- Syringes, IV catheters, and test tubes
- Petri dishes and pipette tips (affordable medical parts).
7.4 Implantable Devices
- Orthopedic components: Knee/hip implant liners (PEEK via injection molding for medical devices).
- Dental implants: Abutments (metal or PEEK, made via MIM or custom medical injection molding).
7.5 Equipment Enclosures
- MRI/CT scanner housings, ventilator casings (large medical enclosures).
- Hospital bed control panels (durable plastic medical parts).

8. FAQ
Medical device injection molding uses medical-grade injection molding plastics, requires a clean room, and adheres to strict standards (ISO 13485, FDA). Standard injection molding lacks these safeguard measures and is therefore not suitable for injection molding medical parts.
Rapid injection molding medical is ideal for prototyping or small-batch runs (for example, testing a new diagnostic device housing). For high-risk injection molding medical devices (such as implants), full-scale production must be carried out using validated medical injection molds and comply with the ISO 13485 standard.
Searching:
- ISO 13485 certification and FDA/EU MDR experience.
- Medical injection molding equipment for cleanrooms.
- Tracking records of the production of your type of injection-molded medical components (for example, blood glucose meter components, dental tools).
- End-to-end services (design, mold making, packaging) to avoid workflow gaps.
Yes, reputable suppliers like YG can provide OEM medical injection molding according to the demands of Europe and America, including UDI labels, aseptic packaging for injection-molded medical shells, and customs documents.
9. Choose YG as Your Medical Injection Molding Supplier
Our Capabilities:
- Full Compliance: ISO 13485 certification, with experience in injection molding medical parts that meet FDA and EU MDR standards.
- One-Stop Service: From custom medical injection molding design (DFM analysis), medical injection mold manufacturing, to cleanroom medical injection molding, sterilization, and packaging.
- Outstanding performance record: Successfully delivered plastic injection-molded medical components for glucose meters, oral care equipment, and surgical tools, with a yield rate of over 99.5%.
- Global Preparation: We understand the demands of the European and North American markets, including aseptic packaging for injection-molded medical shells, UDI labels, and seamless transportation documents.
Let’s cooperate:
Whether you need large-scale medical plastic injection molding for disposable items or custom medical injection molding for new diagnostic equipment, YG has the ability to turn your project into reality. Contact us immediately to get a free DFM analysis and quote.
10. Conclusion
Medical injection molding – a pillar of safe and effective healthcare. Choosing the right medical injection molding supplier means balancing precision, compliance, and scalability, and YG offers all of these.
By prioritizing medical-grade injection molding plastics, cleanroom medical injection molding, and ISO 13485 compliance, you can ensure that your injection molded medical devices meet patient needs and global standards. With YG as your partner, you are ready to bring reliable medical products to market on time and within budget.