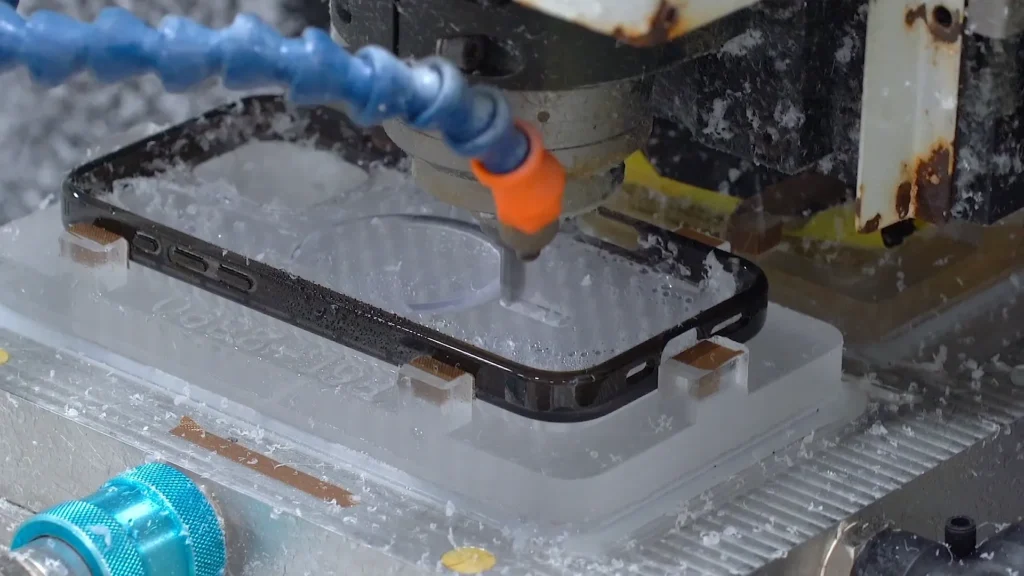
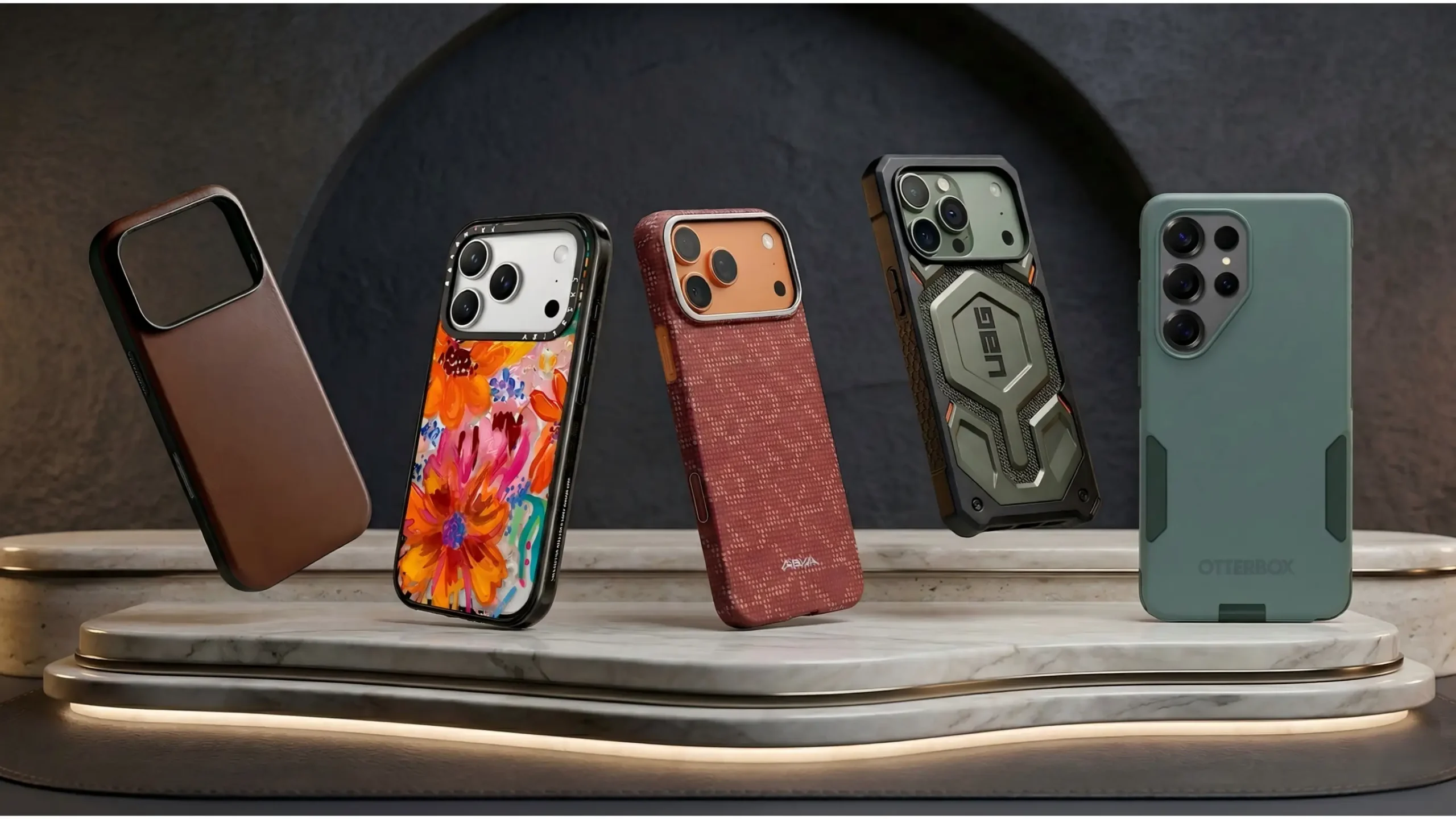
Traditional phone case sampling is slow, expensive, and involves taking weeks to deliver a physical model that may not meet design or functional requirements.
Rapid prototyping (or fast prototyping) has changed this process: transforming digital CAD designs into physical samples within hours or days, rather than weeks. This is the cornerstone for efficiently manufacturing prototypes of mobile phone cases.
This tool enables you to test, iterate, and refine your ideas at a fraction of the traditional cost, which is crucial for remaining competitive in the fast-paced mobile phone accessory market.
What Is a Rapid Prototype?
Table of Contents
ToggleThe definition of rapid prototyping manufacturing is very clear: It refers to a manufacturing process that uses 3D CAD data to generate solid parts, models, or components quickly. Unlike the traditional production method based on molds and focusing on large-scale production, its core lies in rapid iteration and low-cost verification.
For phone cases, this means that customized solutions need to be provided for various materials (TPU, PC, liquid silicone, metal), complex structures (magnetic module camera frames, key openings), and functional requirements – all of which are key elements for achieving seamless prototype development services.
The rapid prototyping process is straightforward: start with DFM (Design for Manufacturability) by using optimized CAD files, select appropriate technologies and materials, create prototypes, test their form and function, and finally complete the design for mass production.
This process ensures that you can identify defects as early as possible, coordinate stakeholders, and confidently advance from the concept stage to production – this is the key to remaining competitive in the phone case market.

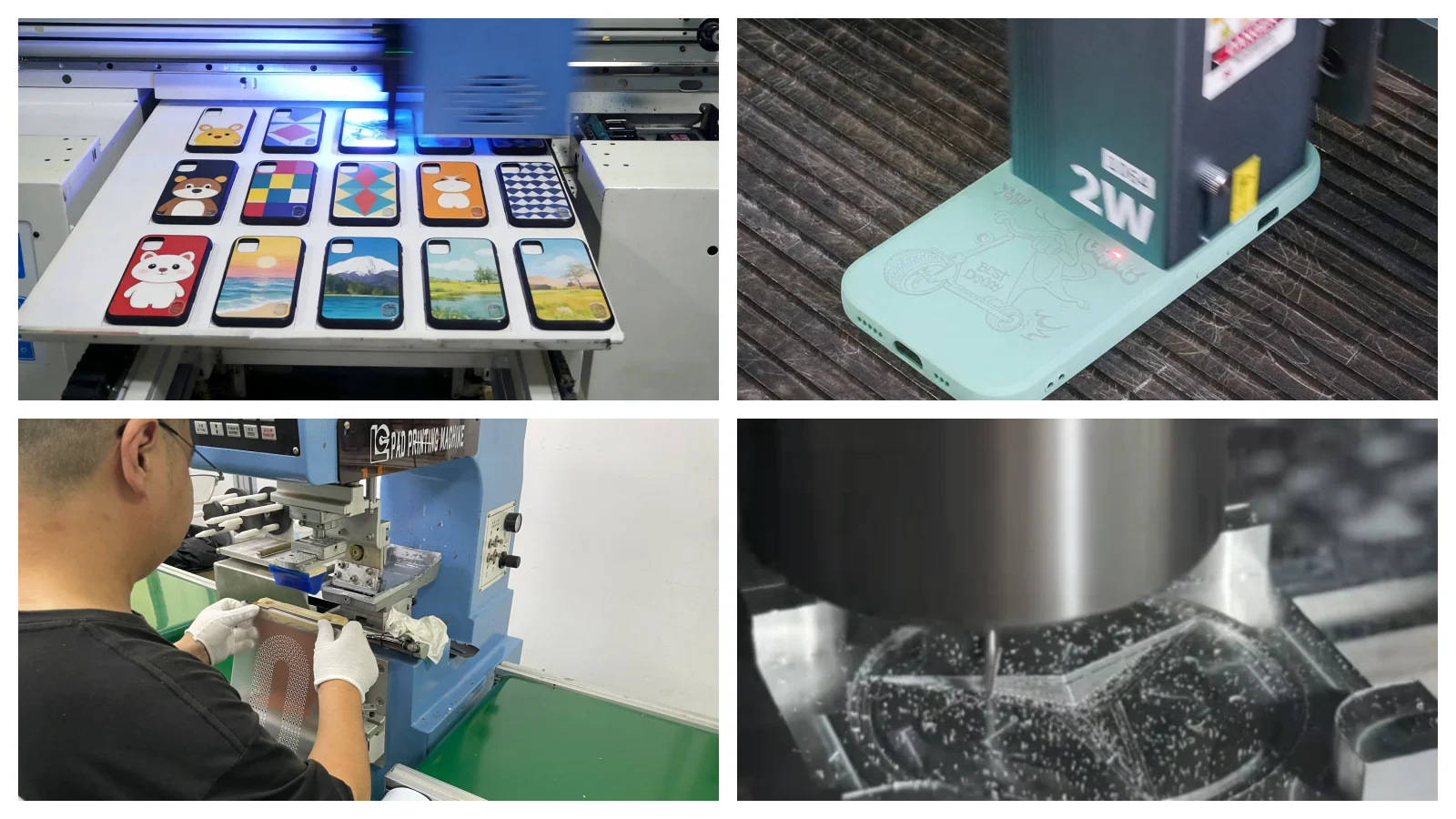
4 Advantages of Rapid Prototyping for Your Phone Case Business
1. Shorten Development Cycles
One of the greatest advantages of rapid prototyping is its speed: traditional sampling may take 2 to 4 weeks, but rapid prototype manufacturing can provide samples within a few hours to 5 working days. This will shorten your time to market by more than 60%.
When mobile phone manufacturers release a new series of products, speed is everything. Fast prototyping enables you to quickly verify the coordination, protection, and design details, so you won’t miss the crucial startup Windows.
2. Lower Trial-and-Error Costs
Rapid prototyping costs are more budget-friendly than traditional methods: the cost per run of a mold ranges from $3,000 to $8,000, while the starting price of rapid prototype options is $200 to $500. Even with multiple iterations, you can still save a lot.
You also need to conduct effective prototype testing as early as possible to identify design flaws such as stuck buttons, wireless charging interference, or insufficient shock absorption. Solving these problems before large-scale production can avoid costly rework.
3. Improve Design Communication & Decision-Making
CAD files are useful, but physical prototypes allow you, your team, and partners to see, touch, and test the product, making manufacturing prototype design services more impactful. This clarity speeds up the alignment.
Feedback becomes actionable: Adjust textures, colors, or structures based on interactions in the real world. This simplifies the decision-making process and fully exploits the value of manufacturing prototypes.
4. Support Customization & Small-Batch Needs
Rapid prototyping enables you to create 10 to 100 custom samples without mold investment, making it highly suitable for IP collaborations, limited editions, or niche market testing.
Whether you need plastic prototype manufacturing or metal options, you can easily switch materials and processes to verify different design directions. This flexibility reduces the risks of customized projects.
Key Rapid Prototyping Technologies & Features
1. 3D Printing (Additive Manufacturing)
| Technology Type | Core Features | Phone Case Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) | Low cost, wide material compatibility (PLA, ABS, TPU), slightly rough surface | Basic shockproof cases, simple structure validation, and low-cost plastic rapid prototyping for all Phone models |
| SLA rapid prototyping (Stereolithography) | High precision (±0.05mm), smooth surface, detailed reproduction | Premium Phone cases, texture validation (matte/embossed), and clear case clarity testing for flagship models |
| Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) | No support structures needed, high part strength, ideal for complex geometries | Phone magnetic case internal structure testing, multi-layer shockproof design validation |
| Selective Laser Melting (SLM) | Metal forming (aluminum prototype, stainless steel), production-grade strength | Phone metal frame cases, high-end business case structure validation |
| Binder Jetting | Multi-part printing, low material cost, suitable for batch concept models | Concurrent Phone design validation, market research samples, and collaboration prototype testing |
| Laminated Object Manufacturing (LOM) | Low cost, no complex post-processing, ideal for large-scale prototypes | iPad cases, large-format outdoor protection case structure validation |
2. Subtractive & Forming Technologies
| Technology Type | Core Features | Phone Case Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| CNC rapid prototyping (CNC Machining) | Wide material compatibility (metal/plastic/wood), high precision (±0.025mm) | Premium Phone metal frame cases, PC hard case structure validation, and stand adapter testing. |
| Sheet Metal Prototyping | Production-grade metal materials (aluminum/steel/stainless steel), high strength | Phone metal cases, protective shell structure validation, load-bearing component testing |
3. Casting & Molding Technologies
| Technology Type | Core Features | Phone Case Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Urethane Casting (Vacuum Casting) | High material simulation (ABS/silicone/elastomer), smooth surface, small-batch replication (10–50 units) | Phone liquid silicone case texture testing, non-slip performance validation, small-batch custom samples |
| Prototype injection molding (Rapid Injection Molding) | Production-grade thermoplastics, consistent process with mass production, and high precision | Pre-mass production Phone case function testing, regulatory compliance samples, small-batch trials (100–500 units) |
Differences Between Rapid Prototyping & Mass Production
In the process of mobile phone case development, rapid prototyping and mass production serve different goals – understanding their differences helps you use them effectively.
1. Core objective
Rapid prototype manufacturing focuses on testing and iteration: verifying the feasibility, functionality, and appearance of a design before it is put into mass production.
Mass production prioritizes efficiency and scalability: producing a large quantity of products at a low unit cost while maintaining consistent quality.
2. Process and cost logic
The rapid prototyping process employs flexible methods, such as 3D printing or small-batch casting. The unit cost is relatively high, but no mold investment is required – ideally 1 to 500 units.
Mass production relies on injection molding or large-scale sheet metal processing. The injection mold cost was very high in the early stage, but the unit cost for orders exceeding 1,000 pieces decreased significantly.
3. Convert value
Rapid prototyping is the bridge to mass production. Through prototype optimization design, increase the output of mass production and reduce the cost of mold adjustment.
FAQs
Q1:What factors affect rapid prototyping cost?
The key factors include prototype size and complexity, material selection (standard plastic/engineering-grade material/metal), technology type (FDM is the most cost-effective, while SLM/ rapid injection molding is more expensive), quantity, and post-processing (sanding, painting, antibacterial coating).
Q2: Are there significant differences in materials and performance between the prototype and the mass-produced phone cases?
We follow the “production-level material matching principle”. For functional testing, we use the same TPU, PC, or liquid silicone as the final product, with very little performance difference. For appearance testing only, we use cost-effective simulation materials and clearly communicate any differences.
Q3:Do you offer eco-friendly materials for rapid prototyping?
A3: Yes. We offer bio-based PLA, recyclable TPU, and biodegradable silicone options for plastic prototyping. These comply with various environmental standards and can be used for ecological certification tests.
Conclusion
Rapid prototyping is not merely a tool – it is a strategic advantage that can shorten time, reduce risks, and increase the success rate of new products.
The various advantages of rapid prototyping are beyond doubt: accelerated product launch, reduced costs, better design verification effects, and the flexibility for customization. It is crucial to collaborate with a manufacturer that is well-versed in the prototype manufacturing process.
As a professional phone case manufacturer, YG offers you comprehensive rapid prototyping services as well as subsequent mass production.
Contact us today for an accurate quote – let us turn your phone case ideas into marketable products faster through our trusted prototype development services!