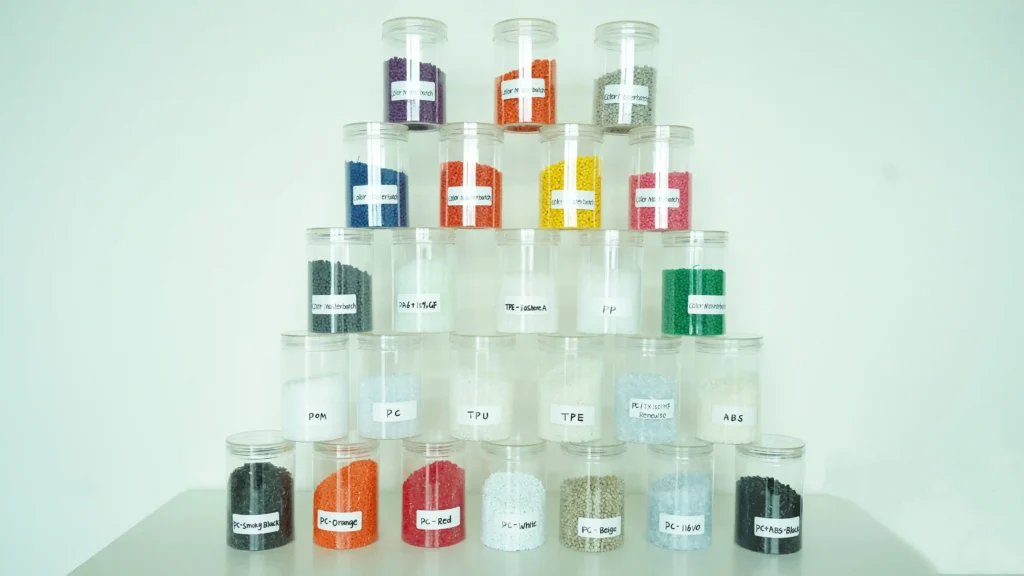
As an injection molding supplier with years of experience, we know that choosing the right plastic material is the key to the success of your project. Whether you are developing consumer goods, industrial components, or medical devices, the materials you choose will directly affect performance, cost, durability, and whether they meet global standards.
In this guide, we will break down the most popular injection molding materials, their key characteristics, and how to choose the material that best suits your needs. Let’s get started!
Common Injection Molding Materials
Table of Contents
ToggleThere are hundreds of plastic resins to choose from, which can easily be overwhelming. However, most projects rely on a few reliable materials, which can be classified into three major categories: general-purpose plastics, engineering plastics, and special functional plastics. Each category addresses different needs, allowing you to quickly narrow down the range of options based on project requirements.
General-Purpose Plastics
These materials are the primary force in injection molding, offering cost-effectiveness, ease of processing, and high suitability for large quantities of everyday products that do not require extreme performance. They strike a balance between affordability and functionality, making them the top choice for brands to expand production.
Polypropylene (PP)
Start with polypropylene (PP) – this is the first choice for those brands that are unwilling to sacrifice performance and focus on cost.
Features: Lightweight and durable, with strong chemical resistance and impressive flexibility. Even after repeated bending or twisting, it can still maintain its shape, and its recyclability makes it a wise choice for eco-conscious enterprises.
Main applications: From packaging and toy parts to home appliance shells and automotive interior components, you will find that the uses of PP are very extensive.
Grades & Brands: For projects that require additional rigidity, high-crystalline PP (HcPP) is an excellent choice. The trusted brand in this field is Mitsubishi Chemical’s Semitron®.

Polyethylene (PE)
Next up is polyethylene (PE) – the most widely used plastic in the world. Its versatility makes it a primary material in countless industries.
Features: Three core types can meet different requirements: HDPE (high-density, rigid), LDPE (low-density, flexible), and PET (transparent, durable). All versions have excellent moisture resistance and chemical resistance, enhancing their appeal.
Main Applications: HDPE shines in food containers and pipes, while LDPE is the perfect choice for flexible packaging and soft toys. PET, with its transparency and strength, is the preferred choice for beverage bottles and pharmaceutical packaging.
Grades and brands: Popular grades include HDPE 500 (high-density) and HDPE 300 (low-density). Leading suppliers such as BASF and DuPont offer stable quality.

Polystyrene (PS)
In addition to general-purpose plastics, polystyrene (PS) is an economical option with unique advantages in specific applications.
Features: There are mainly two types: GPPS (general-purpose, transparent but slightly brittle) and HIPS (high impact, opaque, reinforced with rubber for toughness). PS is moisture-proof, cost-effective and can be sterilized by gamma rays – a key advantage for some industries.
Main applications: PS is frequently used in medical trays, plastic toys, electronic casings, and consumer goods, thanks to the combination of its cost and functionality.
Grade and brand: Reliable brands include PolyRenew® from the American Styrene Company and Polystyrol® from BASF, renowned for their stable performance.

Engineering Plastics
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
For projects that require a balance between strength and multi-functionality, ABS is the preferred choice.
Features: It achieves the best balance between strength, impact resistance, and ease of processing. The color of ABS is very beautiful,l and it supports a series of surface treatments, so you can achieve the appearance you want without affecting performance.
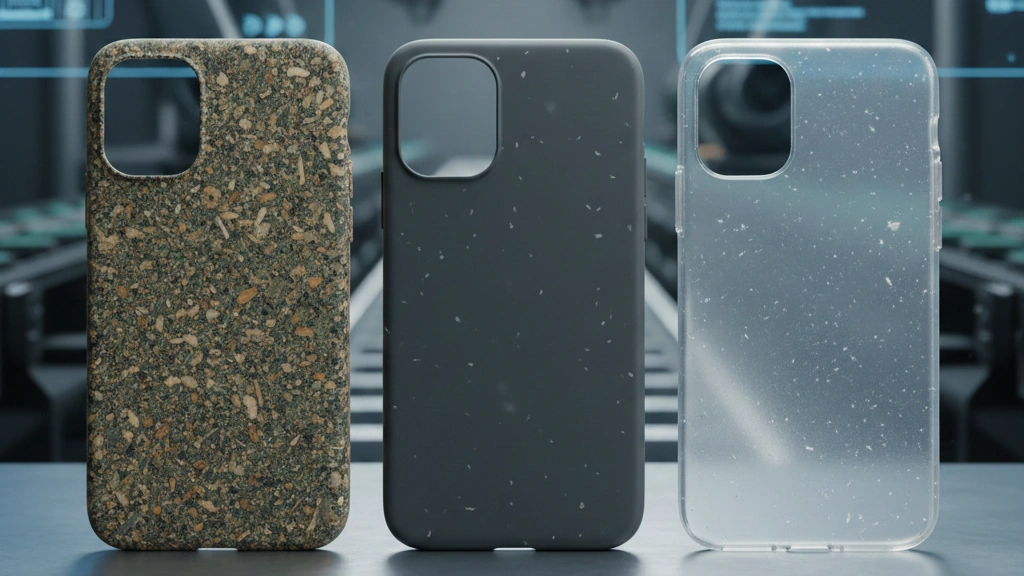
Key applications: From keyboard keys and phone cases to industrial accessories and consumer goods, ABS is everywhere – its adaptability makes it favored by designers.
Grades & Brands: Trusted brands in the ABS field include Samsung Starex®, Toray Toyolac®, and BASF Terluran®, all of which are renowned for their stable quality.

Nylon (Polyamide, PA)
For high-wear and high-stress applications, nylon (polyamide, PA) is hard to surpass.
Features: It has outstanding wear resistance, fatigue strength, and heat resistance, which are crucial for frequently used components. Nylon can also be reinforced with glass fibers to enhance its rigidity and make it more versatile.
Main applications: High-friction components such as gears, bearings, bushings, snap-on closures, and threaded insertions all rely on the durability of nylon.
Grades & Brands: Select professional grades: PA 11 (ideal for outdoor use), PA 12 (low hygroscopicity), PA 46 (high operating temperature), and PA 66 (excellent acid resistance).

Polycarbonate (PC)
If transparency and strength are not negotiable, polycarbonate (PC) is your material.
Features: Sturdy, lightweight, naturally transparent. PC outperforms glass in terms of impact resistance while maintaining crystal-clear optical clarity. It also performs well within a wide temperature range, enhancing its practicality. Note: PC contains bisphenol A, so it is not recommended for food contact applications.
Main applications: Mechanical protection, LED tubes, transparent Windows and medical molds, clear phone cases, etc., all benefit from the unique combination of strength and transparency of PC.
Grades & Brands: SABIC Lexan® offers flame-retardant grades, while Covestro Makrolon® is renowned for its glass-like transparency.

Polyoxymethylene (POM, Acetal)
For precision parts that need to maintain their shape, polyoxymethylene (POM, also known as acetal) is the preferred choice.
Features: It features low friction, extremely low water absorption rate and excellent dimensional stability – all of which are key to parts that require strict tolerances. When necessary, POM can also be strengthened with glass fiber or minerals.
Main applications: Gears, conveyor belts, fasteners, lock systems, and precision mechanical components all rely on the consistent performance of POM.
Grades & Brands: Leading brands include DuPont Delrin® and Ensinger TECAFORM®, which are highly trusted for their reliability in precision applications.

Specialty & Functional Plastics
Acrylic (PMMA)
Acrylic acid (PMMA) is the preferred material for transparent and shatter-resistant components.
Features: A safer alternative to glass, it offers excellent optical clarity and UV resistance, making it highly suitable for components exposed to sunlight. It is also shatterproof, adding an extra layer of security.
Main applications: Windows, greenhouses, solar panels, outdoor signs, and lighting components all benefit from the combination of transparency and durability of acrylic.
Grades & Brands: Choose the universal type, marking grade (higher strength for outdoor use), or Marine grade (waterproof) variant. Top brands include Trinseo PLEXIGLAS® (heat-resistant) and DuPont LUCITE® (high transparency).

Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE)
For parts that require rubber-like flexibility but do not need rubber processing, TPE is the solution.
Features: It combines the processability of plastic and the flexibility of rubber – TPE is easy to stretch and rebound back to its original shape. It is also recyclable and easy to shape, making it a practical option.
Main applications: Medical catheters, automotive seals, footwear, pet products, and shockproof and dust-proof boots all take advantage of the unique properties of TPE.
Grades & Brands: Medical-grade TPE can be used in healthcare applications, with leading brands such as Teknor Apex Telcar® and Kraiburg HIPEX® setting the standard.

Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU)
TPU is an advanced variant of TPE that enhances performance in applications with high-performance requirements.
Features: It features excellent elasticity, ozone resistance, and tolerance to extreme temperatures – outperforming standard TPE under harsh conditions. TPU is also an excellent alternative to hard rubber.
Main applications: Gaskets, casters, electronic enclosures, medical devices (as a PVC alternative), and footwear all benefit from the durability and flexibility of TPU.
Grades and brands: It comes in polyester, polyether, and polycaprolactone grades. Trusted brands such as Lanxess and Lubrizol offer high-quality options.

Comparison of Plastic Injection Molding Materials
| Material | Core Properties | Key Advantages | Typical Applications | Compliance Adaptation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PP | Lightweight, chemical-resistant, recyclable | Low cost, high toughness | Packaging, appliances, automotive parts | FDA, RoHS |
| PE (HDPE/LDPE/PET) | Moisture-resistant, flexible (LDPE) / rigid (HDPE) | Versatile, non-toxic | Food containers, pipes, packaging | FDA, REACH |
| ABS | High strength, impact-resistant, easy to color | Good surface finish | Electronic shells, automotive parts | RoHS, UL |
| PA (Nylon) | Wear-resistant, heat-tolerant, reinforced options | Excellent mechanical performance | Gears, bearings, fasteners | RoHS, REACH |
| PC | Transparent, impact-resistant, wide temperature range | Stronger than glass | Machinery guards, LED light pipes | UL, RoHS |
| PMMA | High transparency, UV-resistant, shatterproof | Superior optical properties | Windows, signage, lighting components | FDA, RoHS |
| TPE | Rubber-like flexibility, recyclable | Easy to process | Medical catheters, seals, pet products | FDA, Medical-grade certification |
| TPU | Elastic, ozone-resistant, extreme temperature tolerance | Durable elasticity | Footwear, gaskets, electronic cases | FDA, RoHS |
| POM | Low friction, dimensionally stable, low water absorption | Precision performance | Gears, fasteners, lock parts | RoHS, REACH |
| PS | Low cost, transparent (GPPS) / impact-resistant (HIPS) | Sterilizable | Medical trays, toys, containers | FDA, RoHS |
Injection Molding Material Selection Guide
- Start with your product’s purpose: What can it do? For high-friction components, nylon or POM should be given priority. For transparent components, choose PMMA or PC. For medical devices, choose FDA-approved TPE or PS.
- Consider environmental conditions: Is it exposed to ultraviolet rays (choose PMMA or UV-stabilized nylon), high temperatures (PC or pa46), or chemical contact (PP or PE)?
- Balance performance and cost: General-purpose plastics (PP, PE, PS) are budget-friendly for high-volume projects. Engineering plastics (ABS, PA) have better performance but are more expensive. Plastics (TPU, PC) are ideal for meeting specific requirements, but they are relatively expensive.
- Verify compliance: Ensure that materials meet the standards of the target market – FDA standards for food contact, RoHS standards for electronic products, REACH standards for chemical safety in the European Union, and medical-grade certification for healthcare products.
Choose YG as your Plastic Injection Molding Manufacturer
As a reliable injection molding supplier, YG is committed to ensuring a seamless connection between your material selection and production process
- Global supply chain: We collaborate with top material manufacturers to source high-quality, traceable resins, so you will never compromise on consistency.
- Expert technical support: Our team helps you select materials, design custom modifications (glass fiber reinforced, flame retardant, colored), and test prototypes before full-scale production.
- Compliance Assurance: All materials comply with global standards (FDA, RoHS, REACH, etc.) and are accompanied by complete compliance certificates, giving you peace of mind.
- Customization capability: Do electronic products require flame-retardant ABS or do tubes need medical-grade TPE? We offer tailor-made material solutions to meet your unique requirements.
FAQ
Q1: Do different materials require different molds?
Yes, high-melting-point materials (such as PC) require heat-resistant molds, while flexible materials (such as TPE) may need specialized tools for proper filling. We will provide you with suggestions on mold compatibility based on the materials you choose.
Q2: How can I confirm that the materials comply with the compliance standards of my market?
We provide detailed compliance reports for each material, including FDA certification for food contact, RoHS certification for hazardous substance limits, and REACH certification for chemical safety. Just share your target market, and we will verify compatibility.
Q3: Will material modification (such as glass fiber reinforcement) significantly increase costs?
The modifications do increase a small portion of the cost, but they usually reduce long-term expenses by enhancing the durability of the product. For bulk orders, we offer competitive custom material prices – contact us for a tailor-made quote.
Q4: Should PMMA or PC be chosen for transparent components?
PMMA is more cost-effective and offers better optical clarity, but PC is stronger and more impact-resistant. Use PMMA for marking or lighting; PC is selected for mechanical protective covers or high-stress transparent components.
Conclusion
The right injection molding material will make your design a high-performance and cost-effective product – working with the right injection molding supplier will make all the difference. Whether you prioritize strength, transparency, compliance, or cost, this guide and our team will provide you with support.
Are you ready for the next step? Contact us immediately for a free consultation on custom material selection or to receive a personalized quote for your project. We will help you find the perfect materials to turn your vision into reality – on time, within budget, and to global standards.
What is your biggest material challenge now? Let us know that we will customize our support according to your needs!