Introduction
Table of Contents
ToggleAre you amazed that phone case manufacturers can produce phone cases with perfect fit, durability, and smooth surfaces? This precision begins with injection molds – tools for mass production. For mobile phone case brands, understanding mold making is not merely about technical knowledge; This is how you ensure consistent quality, avoid defects, and effectively scale up production.
In this guide, we will break down the step-by-step mold-making process, from mold design to mold testing, and share key insights with you.
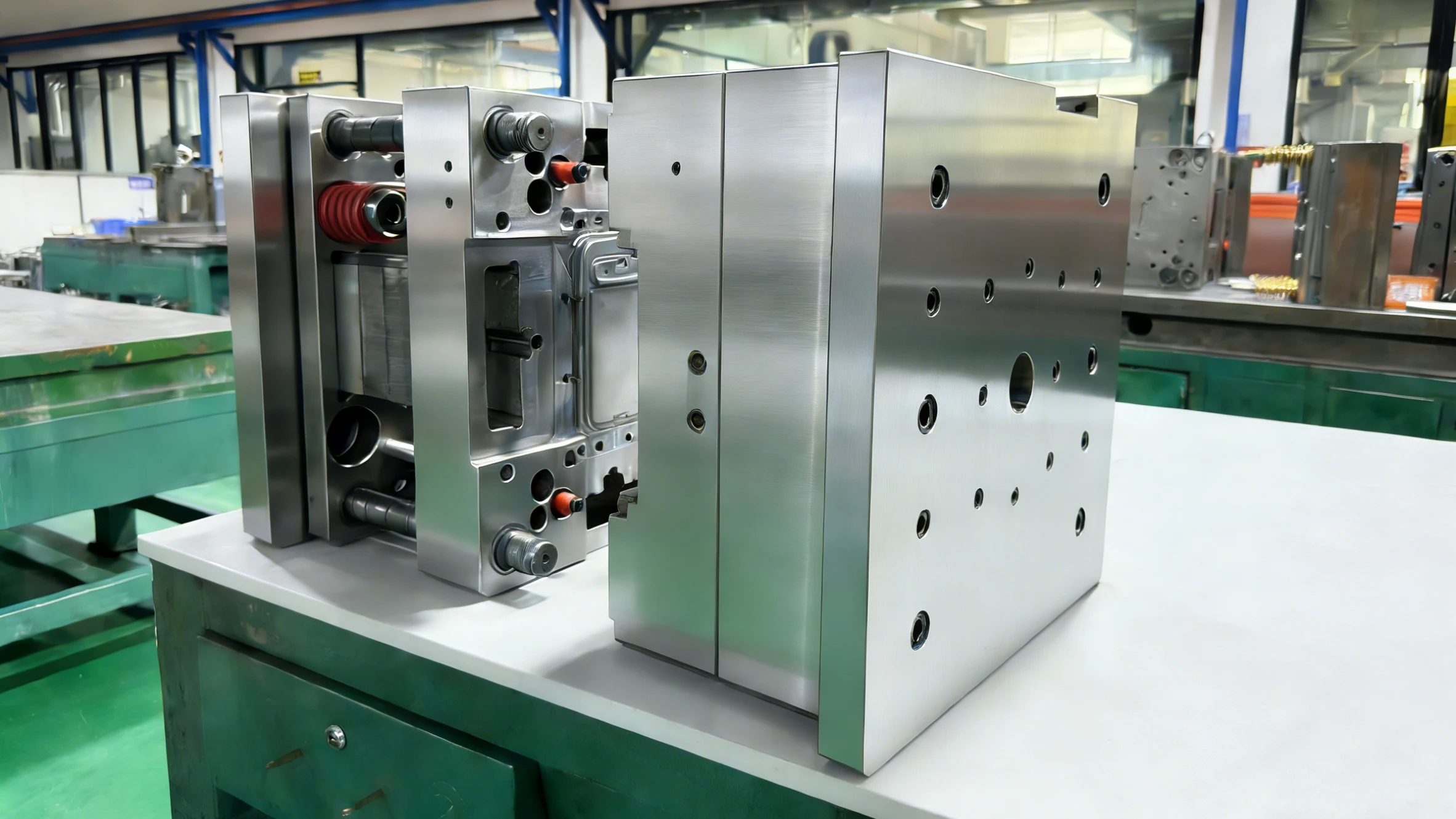
What is a Plastic Injection Mold Tooling?
Plastic injection molding tools are precision tools used for the mass production of plastic products such as mobile phone cases. They are usually made of steel or aluminum. The core principle is to inject molten plastic into the mold cavity, and after cooling and solidification, the shape is formed.
Its core value lies in:
- Achieve high-precision replication of complex structures (such as curved surfaces of mobile phone cases, camera holes, and key positions);
- Support mass production: enhance efficiency, and reduce unit cost;
- Strong material adaptability: suitable for PC, ABS, silica gel, TPU, and other common materials of mobile phone cases.
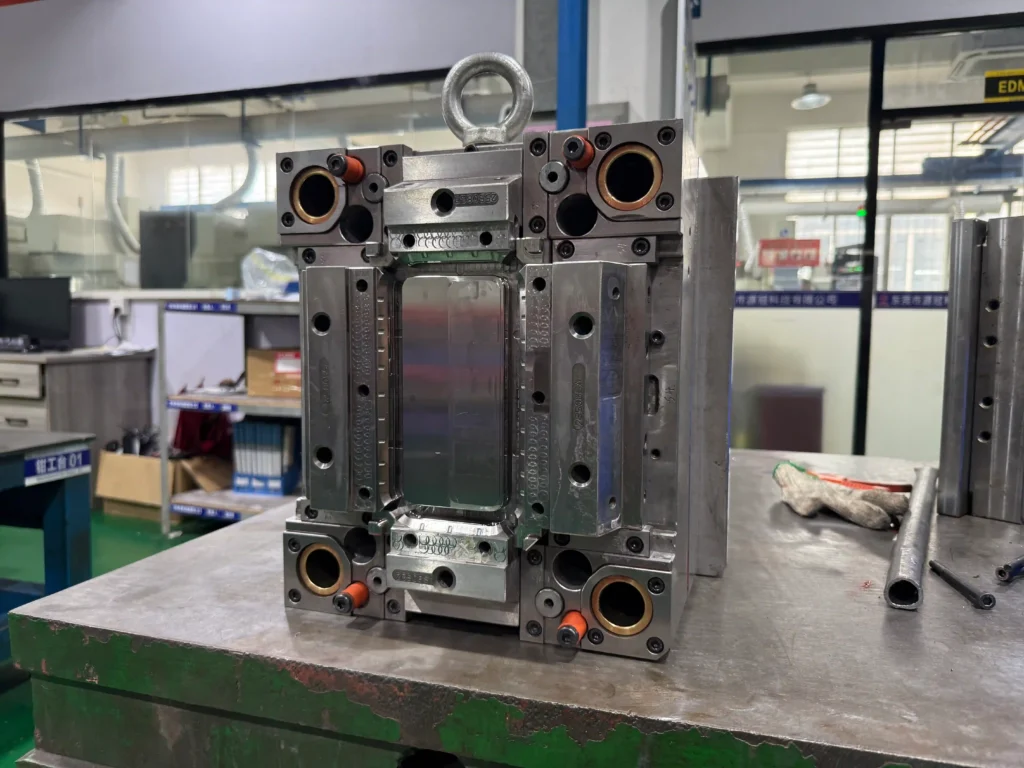

How to Make a Plastic Mold: Step-by-Step
Next, let’s lift the veil on plastic injection mold tools and examine how they have evolved into tools capable of handling large-scale production in injection molding technology.
Step 1: Plastic Mold Design
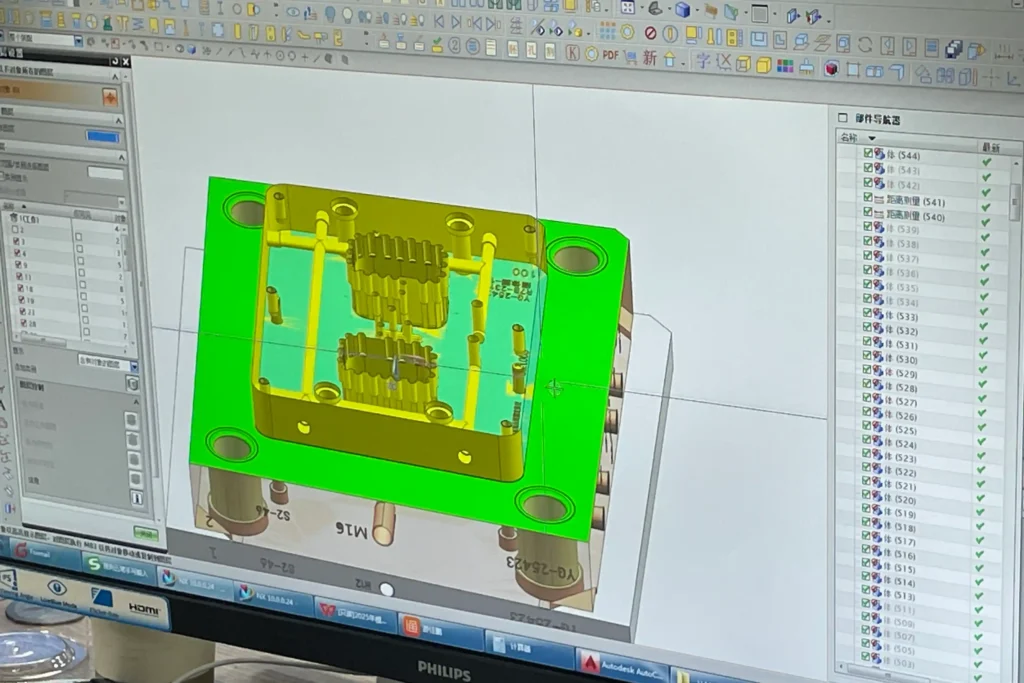
Before making plastic molds, our engineers start with a custom mold design. Based on the product design drawings provided by the client, mold design is carried out using software such as SolidWorks. They draw every curve, cut and texture – even simulate how plastic flows through the mold to avoid defects such as bubbles or uneven cooling.
Hasty design can lead to “dents” (dents on the shell) or “glitters” (ugly plastic excess parts). This is why we run “DFM Check” (Design for Manufacturability) to identify problems as early as possible. For instance, if your design has a sharp corner, we suggest rounding it to prevent cracks from occurring during injection.
Step 2: Material Selection – What Kind of Metal Are Injection Molds Made Of?
Here is a decision that will affect your budget and long-term costs: steel or aluminum?
- Steel plastic molds: This is the main material for plastic injection mold tools. The mold has a lifespan of over 100,000+ cycles, making it an ideal choice for large orders (100,000 + units). If you are going to launch a flagship product that has been a bestseller for many years, this is the perfect choice.
- Aluminum plastic molds: They feature faster processing speed and lower initial costs, making them highly suitable for small-batch production or mold trials, or seasonal designs (such as phone cases with festival themes). But they wear out faster (about 10,000 to 50,000 cycles).
Buyer’s tip: Ask the supplier, “What metal is the injection mold made of and how many cycles can it handle?” If they hesitate, just walk away. At YG, we even share material certificates – transparency is non-negotiable.
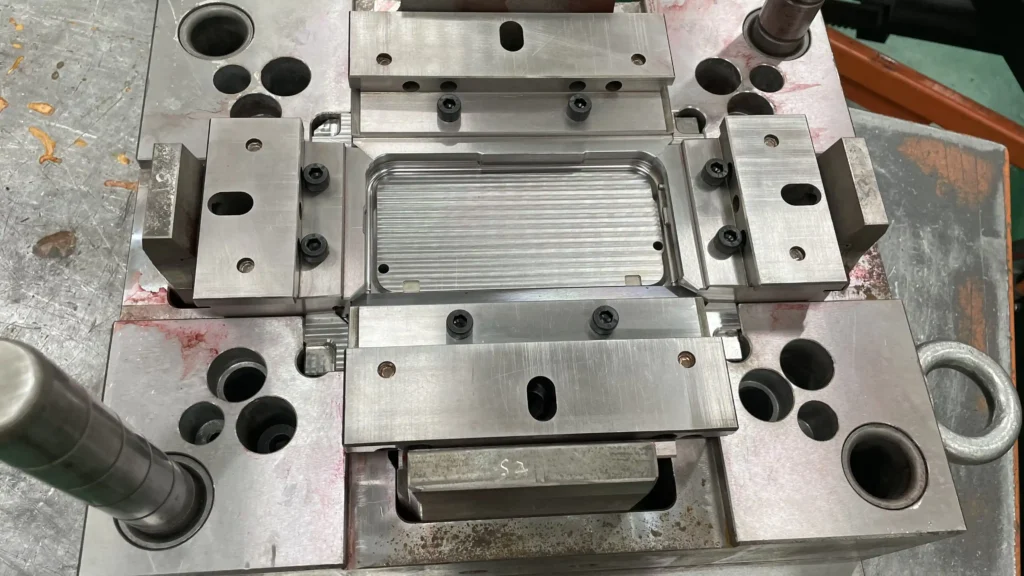
Step 3: Rough Machining and Precision Machining
After determining the mold materials, the next step is to start mold processing. Among them, rough machining and precision forming are the core links, and the two are closely connected to achieve a high-precision structure.
1. Rough processing stage
Material pretreatment and basic forming
According to the customer’s mold life requirements, pre-hardened steel (such as H13 with a hardness of 48-52HRC) is selected. Through quenching and tempering treatment, the material stability is enhanced, and the risk of subsequent deformation is reduced. CNC roughing is carried out using flying knives to quickly remove the excess parts of the blank. A finishing allowance of 0.3 to 0.5mm is reserved for the core structures such as the main cavity, core and slider, while ensuring the reference accuracy of the parting surface.
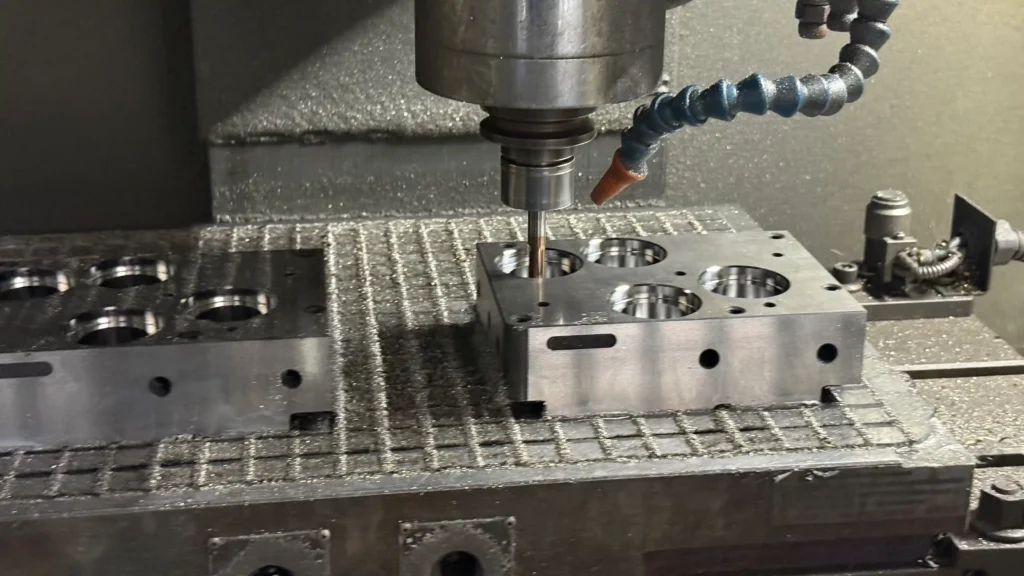

2. Precision Forming Processing stage
CNC precision machining and microstructure treatment
Based on rough machining, complex curved surfaces (such as arc-shaped edges) are processed through high-speed milling, with tolerances controlled within ±0.05mm. For fine structures such as the camera holes in mobile phone cases (hole diameters <1mm), micro-diameter milling cutters are used for fine cutting.
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) and texture realization
For deep grooves or fine textures (such as leather grain, miniature letters) that CNC cannot achieve, the EDM process is adopted, and a precision of ±0.02mm is realized through custom copper electrodes. The special texture on the product surface (such as matte or smooth) is accomplished at this stage through an etching depth of 0.02 to 0.2mm.
Wire cutting and processing of special-shaped parts
Perform wire cutting on irregular inserts such as top pinholes and inclined top guide rails to ensure a fit accuracy of ≤0.01mm and guarantee the coaxiality of the ejection system
Step 4: Post-Machining Finishing – Polishing
Even the best CNC work needs improvement. Here are the methods we use to ensure a flawless surface:
Polishing: Our polishing engineers use diamond gypsum to provide a mirror-like polishing effect (Ra 0.02μm) for the smooth shell. For matte textures, we use chemical etching or sandblasting – this is how injection molding tooling textures create a high-quality feel.
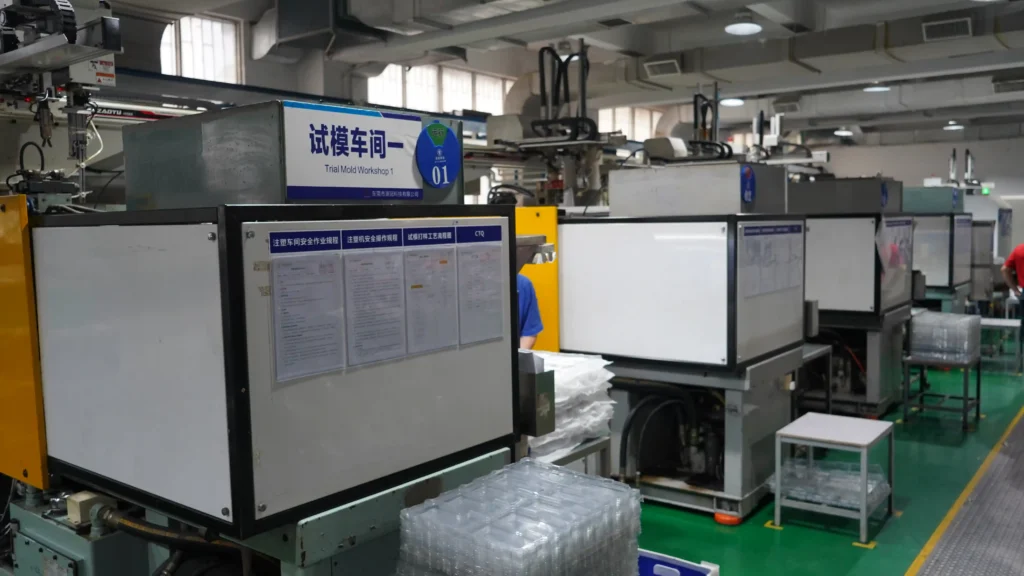
Step 5: Assembly & Testing
An injection mold tooling isn’t just metal—it’s a system of moving parts. We assemble and test rigorously:
- Cooling System Integration: Tiny water channels are drilled to speed up plastic solidification, reducing cycle time by 20% and preventing warping.
- Ejection System Setup: Pins and plates are calibrated to gently push cases out of the mold, avoiding scratches or deformation.
- Trial Runs (T0/T1): We inject plastic (TPU, PC, or a blend) to test for leaks, misalignment, or surface defects. Adjustments are made before mass production—because fixing a mold is cheaper than scrapping 10,000 faulty cases.

The Key Factors Affecting the Quality of Plastic Injection Mold Tools
Not all injection molds are the same. The following are your requirements for the supplier:
Tolerance: Seek an accuracy of ±0.01mm. At YG, we use 3D scanners to verify each mold – there is no “close enough” here.
Lifespan: What is the lifespan of an injection mold? Steel molds should be used continuously for more than 100,000 times and are subject to warranty
Cooling Efficiency: Faster cooling = lower production costs.
Texturing Expertise: How are injection molds textured? We use chemical etching for matte finishes, CNC engraving for logos, or EDM for complex patterns—ensuring your design stands out.
Why Choose YG as Your Injection Mold Maker?
- One-stop service: From custom mold design to delivery, we handle everything. No need to coordinate between the mold manufacturer and the production plant – we are your single point of contact.
- Speed Without Sacrifice: How long does it take to make an injection mold? 35 days (the industry average is 45 days) and 15-day production runs. Do you need 100,000 phone cases for Black Friday? We will meet your deadline.
- More cost-effective injection molds: Our Master Unit Die system enables you to reuse the mold base, reducing the cost of small-batch injection molds by 40%. For bulk orders, we directly save for you through effective molds.
- Reliable quality: Each injection molding tool is inspected several times, and each product is inspected before shipment. We have never had a batch of goods rejected
FAQ
5k–5k–20k for aluminum (small batches), 15k–15k–50k for steel (high-volume). We share detailed quotes after reviewing your design.
Steel molds last 1M+ cycles; aluminum ~100k cycles. We offer free annual maintenance to extend the lifespan.
YG delivers 35-day lead times for standard steel molds (industry average: 45 days) and 15 days for aluminum molds. Our 24/7 mold shop and 23 CNC machines ensure fast turnaround—even for rush orders like holiday-themed cases
Conclusion
A cheap plastic injection mold may save initial funds, but it carries the risks of defects, delays, and damaging customer trust. By collaborating with YG, you will invest in precision, durability, and partnership. With over 30 years of experience and a commitment to quality, we ensure that your molds and mass-produced products, such as phone cases, meet the highest standards – whether you order 1k or 500k.
Are you ready to launch your next bestseller? Contact YG today for a free mold design consultation.

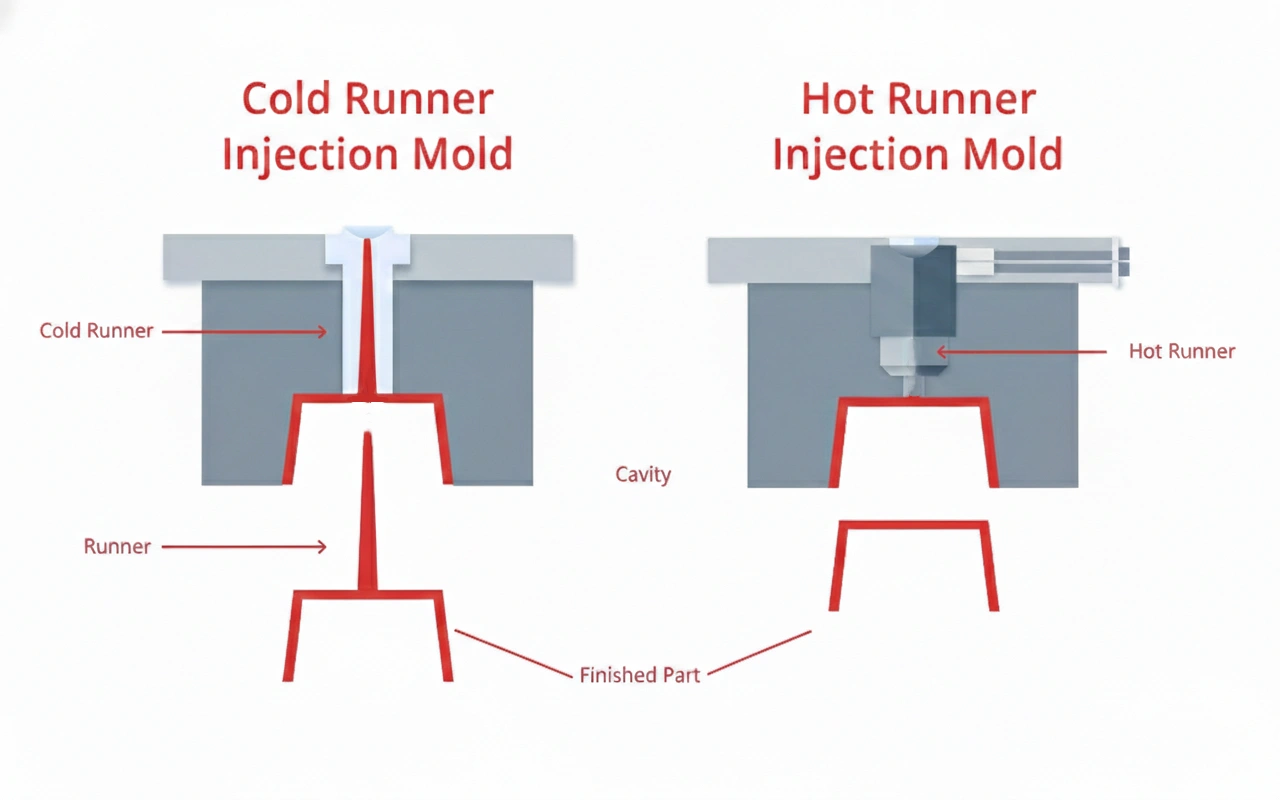

.webp)